November 02, 2006
Authentication in ASP.NET
Authentication is the process of obtaining identification credentials from a user ( such as name and password ), and validating those credentials against some authority.If the credentials are valid, the entity that submitted the credentials is considered an authenticated identity. Once an identity has been authenticated, the authorization process determines whether that identity has access to a given resource.
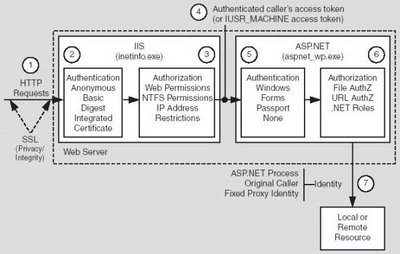
An ASP.net application has two separate authentication layers. That is because ASP.net is not a standalone product. Rather it is a layer on top of IIS. All requests flow through IIS before they are handed to ASP.net. As a result, IIS can decide to deny access without the ASP.net process even knowing that someone requested a particular page. Here is an overview of the steps in the joint IIS and ASP.net authentication process.
1. IIS first checks to make sure the incoming request comes from an IP address that is allowed access to the domain. If not it denies the request.
2. Next IIS performs its own user authentication if it configured to do so. By default IIS allows anonymous access, so requests are automatically authenticated, but you can change this default on a per – application basis with in IIS.
3. If the request is passed to ASP.net with an authenticated user, ASP.net checks to see whether impersonation is enabled. If impersonation is enabled, ASP.net acts as though it were the authenticated user. If not ASP.net acts with its own configured account.
4. Finally the identity from step 3 is used to request resources from the operating system. If ASP.net authentication can obtain all the necessary resources it grants the users request otherwise it is denied. Resources can include much more than just the ASP.net page itself you can also use .Net's code access security features to extend this authorization step to disk files, Registry keys and other resources.
As you can see several security authorities interact when the user requests and ASP.net page. If things are not behaving the way you think they should, it can be helpful to review this list and make sure you have considered all the factors involved
Authentication providers
Assuming IIS passes a request to ASP.net, what happens next? The answer depends on the configuration of ASP.net itself. The ASP.net architecture includes the concept of and authentication provider a piece of code whose job is to verify credentials and decide whether a particular request should be considered authenticated. Out of the box ASP.net gives you a choice of three different authentication providers.
• The windows Authentication provider lets you authenticates users based on their windows accounts. This provider uses IIS to perform the authentication and then passes the authenticated identity to your code. This is the default provided for ASP.net.
• The passport authentication provider uses Microsoft's passport service to authenticate users.
• The forms authentication provider uses custom HTML forms to collect authentication information and lets you use your own logic to authenticate users. The user's credentials are stored in a cookie for use during the session.
Selecting an authentication provider is as simple as making an entry in the web.config file for the application. You can use one of these entries to select the corresponding built in authentication provider:
<authentication mode="windows">
<authentication mode="passport">
<authentication mode="forms">
ASP.net also supports custom authentication providers. This simply means that you set the authentication mode for the application to none, then write your own custom code to perform authentication. For example, you might install an ISAPI filter in IIS that compares incoming requests to list of source IP addresses, and considers requests to be authenticated if they come from an acceptable address. In that case, you would set the authentication mode to none to prevent any of the .net authentication providers from being triggered.
The fig below illustrates the authorization and authentication mechanisms provided by ASP.NET and IIS.
Windows authentication and IIS
If you select windows authentication for your ASP.NET application, you also have to configure authentication within IIS. This is because IIS provides Windows authentication. IIS gives you a choice for four different authentication methods:
Anonymous, basic digest, and windows integrated
If you select anonymous authentication, IIS doesn't perform any authentication, Any one is allowed to access the ASP.NET application.
If you select basic authentication, users must provide a windows username and password to connect. How ever this information is sent over the network in clear text, which makes basic authentication very much insecure over the internet.
If you select digest authentication, users must still provide a windows user name and password to connect. However the password is hashed before it is sent across the network. Digest authentication requires that all users be running Internet Explorer 5 or later and that windows accounts to stored in active directory.
If you select windows integrated authentication, passwords never cross the network. Users must still have a username and password, but the application uses either the Kerberos or challenge/response protocols authenticate the user. Windows-integrated authentication requires that all users be running internet explorer 3.01 or later Kerberos is a network authentication protocol. It is designed to provide strong authentication for client/server applications by using secret-key cryptography. Kerberos is a solution to network security problems. It provides the tools of authentication and strong cryptography over the network to help to secure information in systems across entire enterprise
Passport authentication
Passport authentication lets you to use Microsoft's passport service to authenticate users of your application. If your users have signed up with passport, and you configure the authentication mode of the application to the passport authentication, all authentication duties are offloaded to the passport servers.
Passport uses an encrypted cookie mechanism to indicate authenticated users. If users have already signed into passport when they visit your site, they'll be considered authenticated by ASP.NET. Otherwise they'll be redirected to the passport servers to log in. When they are successfully log in, they'll be redirected back to your site
To use passport authentication you have to download the Passport Software Development Kit (SDK) and install it on your server. The SDK can be found at http://msdn.microdoft.com/library/default.asp?url=/downloads/list/websrvpass.aps
It includes full details of implementing passport authentication in your own applications.
Forms authentication
Forms authentication provides you with a way to handle authentication using your own custom logic with in an ASP.NET application. The following applies if you choose forms authentication.
1) When a user requests a page for the application, ASP.NET checks for the presence of a special session cookie. If the cookie is present, ASP.NET assumes the user is authenticated and processes the request.
2) If the cookie isn't present, ASP.NET redirects the user to a web form you provide
3) You can carry out whatever authentication, checks you like in your form. When the user is authenticated, you indicate this to ASP.NET by setting a property, which creates the special cookie to handle subsequent requests.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home